Candidates for the Backhaul: PBB-TE vs T-MPLS

1. Backhaul looks for candidates
As it was discussed in this article, 4G backhaul needs upgrades. The fourth generation and the increase of bandwidth requirements are the guilty ones. Telecom operators know that it is time to upgrade their mobile backhaul, in order to prepare it for the next generation services and their demands. Wireless incoming technologies, such as WiMAX and LTE (analysis here), are going to be too much for the present backhaul.
Without a proper backhaul optimization, neither your backbone nor your access can stay current. An old fashioned backhaul will be a gigantic bottleneck. Carriers are aware of this fact so they are managing some options to upgrade their Networks.
Which technologies could help carriers to deal with this problem? Lets see a little description of some possible candidates.
2. Candidate 1: Provider Transport Backbone (PBT)
Provider Transport Backbone, also known as PBB-TE (Traffic Engineered Provider Backbone Bridging), is a standard of the IEEE and the ITU-T (802.1 Ethernet working group 802.1Qay).
The objective of PBB-TE is to provide carrier class features over Ethernet networks. The standard implements some of the features of SDH/MPLS into Ethernet. In few words, it can be defined as a “connection oriented packet network“.
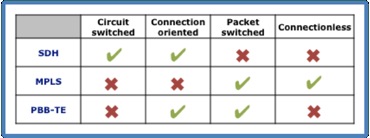
General characteristics of SDH, MPLS, PBB-TE
(To read more and see download options: Click “Read More…” below this line)
Analysis: 4G Backhaul, accept the challenge

1. What is happening with the backhaul?
Numerous statistics and forecasts at Internet show that the use of data services on the mobile phone is growing up very fast. Several factors have helped this growing:
- The increase of smartphones sales in the last 3 years.
- The better performance of 3G-3’5G in comparison with GPRS in terms of download & upload speed.
- The user trends toward web 2.0 and social networks: Facebook, Twitter, FlickR and others have generated the demand of “Internet everywhere” in the users.
Increment of users with data plans
The increase in the number of data traffic users is good news for the telecom carriers, more users mean more money, but this increase also brings them three problems:
- More users mean more data traffic to handle, so carriers need more bandwidth. They have to upgrade their networks: in the access and in the backhaul.
- New services usually require more bandwidth. Web surfing is not sufficient. Telecom operators are facing a big challenge: Users want to watch videos on demand (YouTube, Vimeo…), talk with VoIP services (Skype), listen to real time music (Spootify), etc.
- The ARPU (Average Revenue Per User) seems to be decreasing in the present scenario.
These three facts (and some other ones) start to be a problem to theperformance and to the value of the 3G nets, which are not prepared for such a huge demand of data.
(To read more and see download options: Click “Read More…” below this line)
Analysis of LTE & WiMax

This article tries to describe some comparative points of LTE and WiMax to show their advantages and disadvantages.
1. Time advantage
WiMax is in the market while Long Term Evolution is still in the labs…So, in this point, WiMax has a clear time advantage over LTE: WiMax is present nowadays in numerous countries around the world.
There are already a lot of deployments, and WiMax is growing step by step in different markets, not only in urban zones,but also in rural and/or emerging markets. On the other hand, LTE is still in the labs, and forecasts say that until 2011-2012 (end of 2010 maybe) it will not be in the real market.
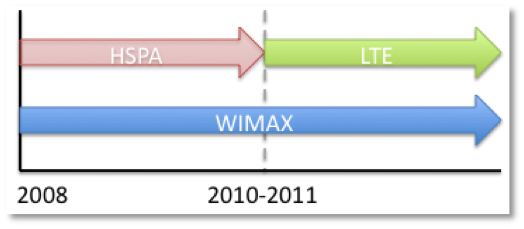
Availability of WiMax, HSPA and LTE
This fact can be an advantage for WiMax, because when LTE has arrived to the telecom market, WiMax will have already a solid market using it’s hardware. However, other technologies, like HSPA+, could decrease that advantage. HSPA+ could compete with WiMax meanwhile LTE arrives.
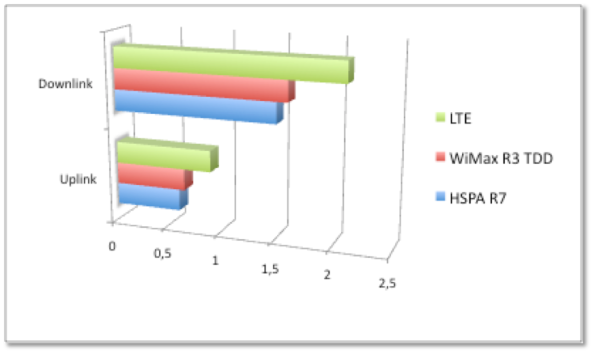
Spectrum efficiency of HSPA, WiMax and LTE in BPS/Hz
As it can be seen in the figure above, HSPA R7 can compete with WiMax R3 TDD in terms of BPS/Hz either in the download link or upload link.
(To read more and see download options: Click “Read More…” below this line)
Basics of LTE (Long Term Evolution)

LTE is the new standard of the 3GPP for the next generation of mobile telecommunications; It is the evolution of GSM/WCDMA. The key features of LTE are:
- OFDM in Download link, DFTS-OFDM (“Single-Carrier FDMA”) in Uplink.
- IP flat architecture with the SAE architecture.
- Low latency (10ms for User-plane, 100ms for Control-plane).
- MIMO antennas.
- Building on current investments in the GSM/UMTS.
- Flexible carrier bandwidths: 1.4MHz -20MHz. (1.4, 3, 5, 10, 15 and 20 MHz).
- FDD – TDD.
- LTE can do handover and roaming to existing networks.
- DL-peak: max 326,4 Mbit/s with 4×4 antennas, 172,8 Mbit/s with 2×2 antennas.
- UL-peak: Max 86,4 Mbit/s.
- Up to 200 users at the same time in a 5 MHz cell.
- Average optimum cell distance 5km. Cell of 30km still works good, with a little degradation. Cell of 100km is still acceptable.
- Increased spectrum flexibility, It supports spectrum slices of 1.5 MHz (up to 20 MHz).
Basics of WiMax (Worldwide Interoperability Microwave Access)

WiMax is a broadband wireless technology. It was developed by the WiMax Forum in the last years and It is based on the 802.16 standard which has the objective of provide high speed data transfers over the air.
Some of the possible uses of WiMax are:
- As an alternative to DSL at the “last mile”.
- As an alternative to the backhaul and access of 2G, 3G, 3’9G infrastructure.
- As an alternative option to connect rural areas to Internet where there are not any telecom infrastructure or when It is not easy to deploy it (For example in rural or disaster areas).